| VANADYL NAPHTHENATE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 68553-60-6 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 271-395-7 | |
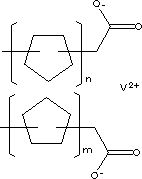
| FORMULA | [(CH2)nCOO]2V | |
| MOL WT. | ||
|
H.S. CODE |
3824.20 | |
| TOXICITY | ||
| SMILES |
| |
| CLASSIFICATION |
| |
| SYNONYMS | Vanadium Naphthenate Oxide; | |
| Naphthenic acids, vanadyl complexes; Naphthensäuren, Vanadyl Komplexe (German); ácidos nafténicos, complejos de vanadilo (Spanish); Acides naphténiques, complexes de vanadyle (French); | ||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | green oily liquid | |
| MELTING POINT | ||
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.04 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | ||
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2 Flammability: 0 Reactivity: 0 | |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
| FLASH POINT | 30 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Moisture sensitive | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Naphthenic acid
is a complex of carboxylic acids( various low-molecular-weight fatty acids,
believed to have cyclopentane ring mainly.) obtained as a by-product of
petroleum refining; with a variable composition and ingredients; generally 180
- 350 mole wt. It is used in deicing, dust control, wood preservative and road
stabilization. Naphthenic acid and metallic naphthenates have industrial
applications in synthetic detergents, solvent additives for paint, varnish, oils
and resins. They are used as lubricants, corrosion inhibitors and fuel
additives. They are used as wood preservatives; catalysts; insecticides; wetting
agents; lubricating oil additive.
Paint driers are substances put into paint to make dry quickly. They are metallic salts of low-molecular-weight (chiefly C8) fatty acids or naphthenic acids. Naphthenic acid is a complex of carboxylic acids( various low-molecular-weight fatty acids believed to have cyclopentane ring mainly). Hydrocarbon parts take oxygen in air and metals act as catalyst to speed up the oxidative coating. Cobalt is the most useful. It is a powerful oxidation catalyst and can keep whiteness. Auxiliary metals should be added to prevent surface wrinkling after drying. Primary metals which can replace for cobalt are zirconium, lead, cerium and iron and auxiliary metals are like calcium, manganese, barium, zinc, lithium. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
green oily liquid | |
| METAL CONTENT |
3.8 - 4.2 or 1.8 - 2.2% | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 50kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing Group: II) | |
| UN NO. | 2931 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 26 | ||
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF VANADIUM AND ITS COMPOUNDS | ||
|
Vanadium a soft, ductile, silver-grey metallic transition element in the
member of group Vb of the periodic table; symbol V; Atomic number 23; atomic
mass; 50.9415; melting point ca 1,890 C; boiling point ca 3,380 C; specific
gravity about 6 at 20 C; valence +2, +3, +4, and maximum +5; electronic config
[Ar]3d34s2; resembles chromium in properties; found in several minerals such as
carnotite, patronite, roscoelite, and vanadinite with good structural strength.
Vanadium has two natural isotopes, 50v and 51v, and several radioactive
isotopes (46-49V, 52-54V) have been obtained artificially. It dissolves in
water to form acidic solutions and dissolves in acids. It reacts with bases to
form vanadates. Vanadium trioxide (V2O3) is basic in solution and dissolves in
acids to give the green hexa-aquo ion (V(H2O)6)3+. In solution, V3+ is a strong
reducing agent and slowly attacks water with the production of hydrogen.
Vanadium is usually found bound to oxygen as a negatively charged polymeric
oxyanion that tends to complex to polarizable ligands, such as phosphorus and
sulfur. Vanadium can be obtained by the extraction from ores, extraction from
fossil fuels and extraction from slag . It has good resistance to corrosion by
hydrochloric and sulfuric acids, saltwater, or alkalies at room temperature but
oxidizes readily above 660 C. Vanadium has good structural strength and a low
fission neutron cross section, making it useful in nuclear applications. It is
intermediate between the metals and the non-metals, having either an
electronegative or an electropositive metal results in numerous chemical
compounds including vanadates and complex organic compounds. The principal use of
vanadium is in alloys, where almost three quarters of all vanadium produced is
used as additive in making special steels. It is a powerful alloying agent; a
small amount adds strength, toughness and heat resistance. It is added to steel
in the form of either ferrovanadium (vanadium-iron alloy) or vanadium carbide.
Vanadium is also a major alloying element in titanium alloys for high-strength.
Non-ferrous metals alloys are used in the atomic energy industry, aircraft and
space technology due to its low fission neutron cross section. Vanadium
disilicide is used in the production of high-temperature refractory products.
Vanadium-aluminum-titanium alloys are used in high-speed airframes and jet
engines. Vanadium chemical compounds such as vanadium oxides and various
vanadates are used as catalysts for the synthesis of sulfuric acid (the oxidation of SO2 to SO3) and maleic
and phthalic anhydride, the oxidation reaction of organic compounds
including ethanol to acetaldehyde
and
petroleum cracking. They are used in the manufacture of
polyamides (nylon), sugar to oxalic acid and anthracene to
anthraquinone. They are used as catalytic converters for the exhaust gases
of internal combustion engines. They also have applications in producing glass
and enamels, organic ion exchangers, luminescent compounds, synthetic rubbers, thermistors and switching elements as well as in producing
paints, as developers, sdepolarizers, and colouring agents in photography and
cinematography. They are used in inhibiting UV light
transmission in glass. Vanadium compounds are used as mordants in the dyeing and
printing of fabrics, particularly for fixing aniline black on silk (in form of ammonium vanadate)
and
cathode-ray tubes. Europium-activated yttrium vanadate is used in colour
television tubes. Vanadium hydride can be used as a neutron moderator in atomic
reactors. Soluble salts of arsenous-vanadous acid have been used as
fungicides and insecticides. Vanadium slags are used in casting shops as a
moulding material to improve the quality of the casting surface and to
facilitate cleaning.
|
||